what is relay
Understanding Relays: The Hidden Heroes of Electrical Control
Introduction
Relays might not be as flashy as the latest gadgets or as prominent as smartphones, but they play a crucial role in our daily lives. These unassuming devices are the unsung heroes of electrical control, allowing us to automate, control, and safeguard various processes. In this blog post, we'll dive deep into the world of relays, exploring what they are, how they work, and their numerous applications.
What is a Relay?
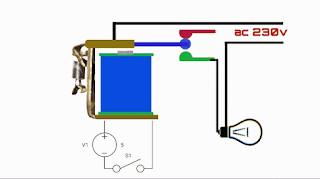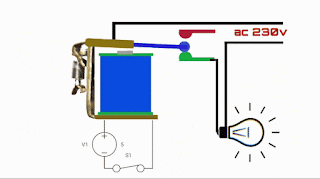
A relay is an electromechanical device that acts as a switch controlled by an electrical signal. It consists of three main components:
1. **Coil**: The coil is an electromagnetic winding made of wire, which generates a magnetic field when current flows through it.
2. **Contacts**: The contacts are the actual switches inside the relay, and they are typically made of metal. These contacts open or close in response to the magnetic field created by the coil.
3. **Actuator**: The actuator is responsible for physically moving the contacts when the coil is energized or de-energized.
How Does a Relay Work?
The operation of a relay can be summed up in three simple steps:
1. **Energizing the Coil**: When an electrical current is applied to the coil, it generates a magnetic field.
2. **Contact Movement**: The magnetic field produced by the coil attracts the actuator, which, in turn, moves the contacts. When the coil is de-energized, the contacts return to their original position.
3. **Controlled Circuit**: The movement of the contacts inside the relay controls an electrical circuit separate from the coil's circuit. This allows a low-power signal to control a high-power circuit, making relays ideal for applications where electrical isolation or amplification is needed.
Types of Relays
Relays come in various types, each designed for specific applications:
1. **Electromechanical Relays**: These are the traditional relays we described above, with a coil, contacts, and an actuator. They are reliable but may have slower switching times compared to other types.
2. **Solid-State Relays (SSRs)**: SSRs use semiconductor devices like thyristors and transistors to switch high-power loads. They are faster, more durable, and have no moving parts.
3. **Reed Relays**: Reed relays use magnetic fields to control the opening and closing of reed switches. They are compact and suitable for high-frequency applications.
Applications of Relays
Relays are incredibly versatile and find applications in various industries and scenarios, including:
1. **Automotive**: Relays are used in cars to control various functions, such as turning on headlights, activating the starter motor, and managing power windows.
2. **Industrial Automation**: In factories and manufacturing plants, relays are essential for controlling machinery, conveyor belts, and other automated processes.
3. **Home Automation**: Relays are at the heart of home automation systems, controlling lighting, HVAC systems, and security devices.
4. **Telecommunications**: In the telecom industry, relays are used in switching equipment and network infrastructure.
5. **Safety Systems**: Relays are critical components in safety systems, like emergency shutdowns and fire alarms.
Conclusion
Relays may be small and unassuming, but their impact on our lives is immense. They bridge the gap between low-power control signals and high-power loads, enabling automation and safety in countless applications. Next time you flick a switch or start your car, take a moment to appreciate the hidden hero behind the scenes - the relay.









Comments